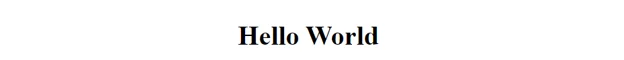Introduction
Today, front-end frameworks and libraries are becoming an essential part of the modern web development stack. React.js is a front-end library that has gradually become the go-to framework for modern web development in the JavaScript community.
What is React.js?
React.js is an open source JavaScript library carefully crafted by Facebook that aims to simplify the complex process of building interactive user interfaces. Think of a user interface built with React as a collection of components, each responsible for outputting a small, reusable piece of HTML code.
In React, you develop your applications by creating reusable components, which you can think of as independent Lego blocks. These components are individual pieces of a final interface that, when assembled, form the entire user interface of your application.
React's primary role in an application is to manage the view layer of that application by providing the best and most efficient rendering implementation, much like the V in the Model-View-Controller (MVC) pattern. Instead of addressing the entire user interface as a single unit, React.js encourages developers to break down these complex user interfaces into individual reusable components that form the building blocks of the entire user interface. In doing so, the ReactJS framework combines the speed and efficiency of JavaScript with a more efficient way to manipulate the DOM to render web pages faster and create highly dynamic and responsive web applications.
A brief history of React.js
In 2011, Facebook had a large user base and was faced with a challenging task. It wanted to provide a richer user experience to its users by creating a more dynamic and responsive interface that was faster and more efficient.
Jordan Walk, a software engineer at Facebook, created React to do just that. React simplified the development process by providing a more organized and structured way to create dynamic, interactive user interfaces with reusable components.
Facebook's News Feed was the first to use it. With its revolutionary approach to DOM manipulation and user interfaces, React dramatically changed Facebook's approach to web development and quickly became popular in the JavaScript ecosystem after its release to the open source community.
What does React.js do?
Typically, you request a web page by typing its URL into your web browser. Your browser then sends a request for that web page, which your browser serves. If you click a link on that web page to go to another page on the website, a new request is sent to the server to get that new page.
This back-and-forth loading pattern continues between your browser (client) and the server for every new page or resource you try to access on a website. This typical approach to loading websites works well, but consider a very data-intensive website. Reloading the entire web page back and forth would be redundant and create a poor user experience.
Furthermore, when data changes in a traditional JavaScript application, it requires manual manipulation of the DOM to reflect those changes. You have to identify which data has changed and update the DOM to reflect those changes, which results in a page reload.
React takes a different approach by allowing you to build what is known as a Single Page Application (SPA). A Single Page Application loads a single HTML document on the first request. It then updates the specific section, content, or body of the web page that needs updating using JavaScript.
This pattern is known as client-side routing because the client does not have to reload the entire web page every time the user makes a new request to get a new page. Instead, React breaks down the request and fetches only the parts that need to change, making the changes without having to reload the entire page. This approach results in better performance and a more dynamic user experience.
React relies on a virtual DOM, which is a copy of the real DOM. React's virtual DOM is immediately reloaded to reflect the new change whenever there is a change in the data state. React then compares the virtual DOM to the real DOM to figure out exactly what has changed.
React then finds the least expensive way to patch the actual DOM with that update without rendering the actual DOM. As a result, React components and UIs reflect changes quickly because you don't have to reload the entire page every time something is updated.
How to use React.js
Unlike other frameworks like Angular, React doesn't impose strict rules on code conventions or file organization. This means that developers and teams are free to set the conventions that work best for them and implement React however they see fit. With React, you can use as much or as little of it as you need because of its flexibility.
Using React, you can create a button, a few pieces of an interface, or your entire app's UI. You can gradually adopt and integrate it into an existing application with some interactivity, or better yet, use it to build powerful React apps from the ground up, depending on your needs.
Integrating React into an existing website
When you’re looking to add dynamic interactivity to your website, React is a great choice. By integrating React, you can create reusable, interactive components that can be placed anywhere on your site, such as sidebars or widgets. Here’s a simple breakdown of the steps to achieve this.
Step 1: Add CDN scripts to HTML
- Start by adding the React core library API from the CDN to your website's HTML index file.
- Then import the React DOM from the CDN. This is necessary to render the components to the Document Object Model (DOM).
- Next, add Babel from the CDN, which translates React code to ensure compatibility between browsers. Also, don't forget to upload your React component file.
The first step is to add two main CDN scripts to your website's HTML index file. You'll need these scripts to load React into your application via the CDN service.
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react@17/umd/react.development.js" crossorigin></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@17/umd/react-dom.development.js" crossorigin></script>
<script src='https://unpkg.com/[email protected]/babel.js'></script>
<script type="text/babel" src="like_widget.js"></script>
Step 2: Mark the render location on your website
Determine the location in your HTML where the React component will be rendered. This can be done by adding an element <div> It did so with a unique identifier, which we will reference in our React code.
<!-- ... Your existing HTML markup ... -->
<div id="like_widget_container"></div>
<!-- ... Your existing HTML markup ... -->
Step 3: Build the React component
- Create a React component in this case called like_widget.js.
- This component will have a simple function that returns a JSX statement that renders the message “Hello World”.
- With the help of ReactDOM, we then render this component to the DOM, targeting the unique ID we set earlier in our HTML.
// Custom React component function that returns a JSX syntax
const ActualWidget = () => Hello World;
// Select the container
const container = document.getElementById("like_widget_container");
// Render the component to the DOM
ReactDOM.render(, container);
If you run the program, it will display “Hello World” to the browser at the exact spot you marked in the image below.
You may have noticed a strange syntax called JavaScript XML (JSX) returned by the ActualWidget function. You use JSX with React to easily combine HTML and JavaScript. Facebook developed JSX as a syntax extension for JavaScript to extend the functionality of HTML by embedding it directly into JavaScript code. With JSX, there is no need to separate HTML and JS code, because React allows you to write declarative HTML directly into JavaScript code.
Creating a full-fledged React App
While you can easily drop React into an existing web app to create small pieces of an interface, it's more practical to use React to build full web apps. However, React does have some heavy tool configuration requirements that are often daunting and tedious to set up when creating new React apps.
Fortunately, you don't need to learn these build settings or configure the build tools yourself. Facebook has created a Node command-line tool called cre-react-app to help you build a React app. This package helps you do this out of the box and provides a consistent structure for React apps that you'll recognize when you move between React projects.
Creating a new React project is as simple as running the following commands in your terminal:
npx create-react-app my-new-app
cd my-new-app
npm start

React.js examples
As the genesis of React.js, Facebook is an example of the library’s prowess. React simplifies the platform’s real-time features such as likes, comments, and status updates, ensuring a seamless and dynamic user experience. React’s modular nature facilitates Facebook’s constantly evolving interface and adapts to the needs of its more than 2.8 billion monthly active users.
Instagram Web is a canvas of interactive elements, all powered by React.js. Every image, like the story view and direct message, emphasizes React’s ability to quickly handle complex user interactions. The platform’s beautiful, user-friendly interface is a testament to React’s skill at delivering high-performance interactions.
Netflix
Airbnb shows how React.js can transform complex data into an intuitive user experience. Each property listing, interactive map, and real-time booking are a symphony of React components that work in harmony to create a seamless user journey from browsing to booking.