Introduction
Python data types are used to define the type of a variable. In this article, we will list all the data types and discuss the functionality of each. If you are just starting out with Python, don't forget to check out our Python tutorial for beginners first. And if you have already done so, don't forget to check out our previous tutorial on Python comments and statements.
Python numeric data type
Python numeric data type for storing numeric values such as;
- int – Holds signed integers of unlimited length.
- long - holds long integers (present in Python 2.x, deprecated in Python 3.x).
- Float – Holds exact floating point numbers and is accurate up to 15 decimal places.
- Mixed – contains mixed numbers.
In Python, we don't need to define the data type while defining a variable like in C or C++. We can simply assign values to a variable. But if we want to see what type of numeric value it currently holds, we can use type(), like this:
#create a variable with integer value.
a=100
print("The type of variable having value", a, " is ", type(a))
#create a variable with float value.
b=10.2345
print("The type of variable having value", b, " is ", type(b))
#create a variable with complex value.
c=100+3j
print("The type of variable having value", c, " is ", type(c))If you run the above code, you will see output like the image below.

Python string data type
A string is a sequence of characters. Python supports Unicode characters. Generally, strings are represented with single or double quotes.
a = "string in a double quote"
b= 'string in a single quote'
print(a)
print(b)
# using ',' to concatenate the two or several strings
print(a,"concatenated with",b)
#using '+' to concate the two or several strings
print(a+" concated with "+b)
The above code produces output like the image below.

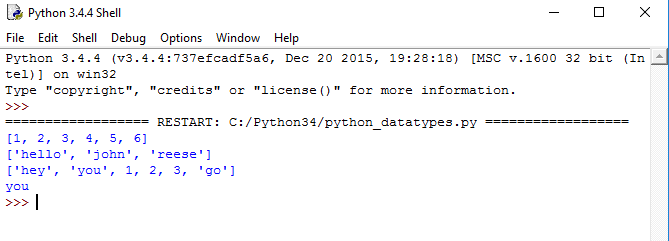
Python List Data Type
This list is a versatile data type exclusive to Python. In a sense, it is the same as an array in C/C++. But the interesting thing about a list in Python is that it can hold different types of data at the same time. A formal list is an ordered sequence of some data written using square brackets ([]) and commas (,).
#list of having only integers
a= [1,2,3,4,5,6]
print(a)
#list of having only strings
b=["hello","john","reese"]
print(b)
#list of having both integers and strings
c= ["hey","you",1,2,3,"go"]
print(c)
#index are 0 based. this will print a single character
print(c[1]) #this will print "you" in list c
The above code produces output like this

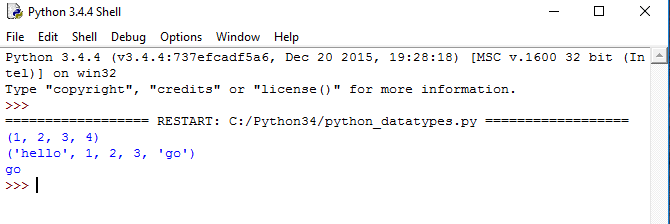
Python Tuple
Tuple is another data type which is a sequence of data similar to a list. But it is immutable. This means that the data in a tuple is write-protected. The data in a tuple is written using parentheses and commas.
tuple having only integer type of data.
a=(1,2,3,4)
print(a) #prints the whole tuple
tuple having multiple type of data.
b=("hello", 1,2,3,"go")
print(b) #prints the whole tuple
#index of tuples are also 0 based.r code... */The output of this Python data type tuple example code above will be as shown below.

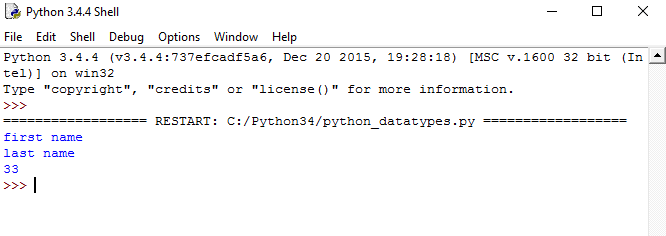
Python Dictionary
A Python dictionary is an unordered sequence of data in the form of key-value pairs. It is similar to a hash table. Dictionaries are written in curly braces in the form key:value. It is very useful for retrieving data in an efficient way among large amounts of data.
#a sample dictionary variable
a = {1:"first name",2:"last name", "age":33}
#print value having key=1
print(a[1])
#print value having key=2
print(a[2])
#print value having key="age"
print(a["age"])If you run this Python dictionary data sample code, the output will be like the image below.

Result
So that's all for today about Python data types. Don't forget to run each piece of code on your machine. Also, don't just copy-paste. Try writing the lines of code yourself.