Introduction
GitHub is a cloud-hosted Git management tool. Git is a distributed version control, meaning the entire repository and history lives wherever you put it. People tend to use GitHub in their business or development workflows as a managed hosting solution to back up their repositories. GitHub takes this even further by allowing you to connect with colleagues, friends, organizations, and more.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to take an existing project you are working on and push it to GitHub.
How to push an existing project to GitHub
- Create a new GitHub Repo
- Launch Git in the project folder.
- Set up the Git Repo
Prerequisites
To initialize the repository and push it to GitHub, you need the following:
- A free GitHub account
- git is installed on your local machine
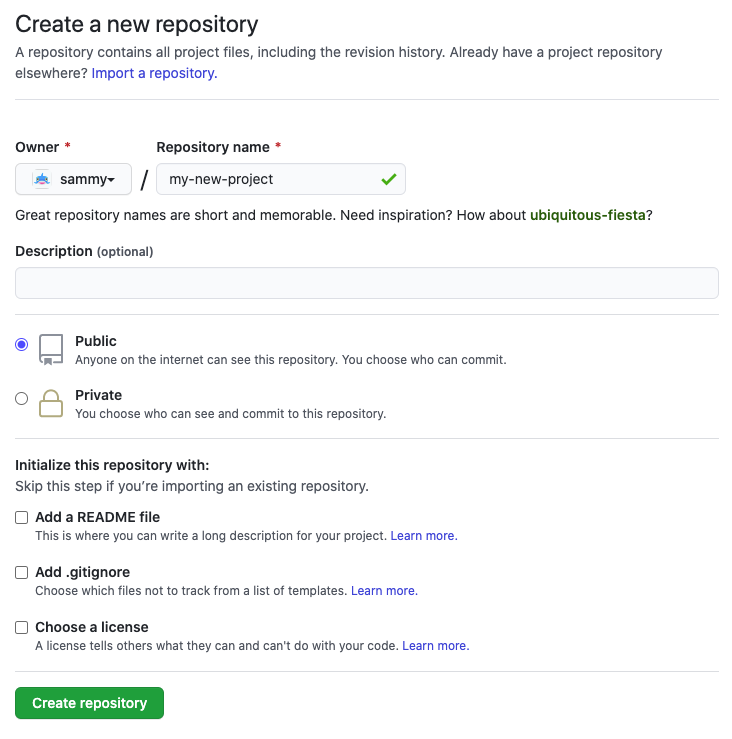
Step 1 – Create a new GitHub repository
Log into GitHub and create a new empty repository. You can choose whether to initialize a README or not. This doesn't really matter because we're just going to overwrite everything in this remote repository anyway.
Step 2 – Launch Git in the project folder
From your terminal, after navigating to the folder you want to add, run the following commands.
Step 3 – Set up the Git Repo
Make sure you are in the root directory of the project you want to push to GitHub and run:
git initThis step creates a hidden .git directory in your project folder that the git software recognizes and uses to store all the metadata and version history for the project.
Add files to the Git directory
git add -AThe git add command is used to tell git which files to include in a commit, and the -A (or –all) argument means “include all.”.
Commit the added files.
git commit -m 'Added my project'The git commit command creates a new commit with all the files that were "added". -m (or -message) sets a message that will be included with the commit and used for future reference to understand the commit. In this case, the message is: "I added my project".
Add a new remote source
git remote add origin [email protected]:sammy/my-new-project.gitIn git, a “remote” refers to a remote version of the same repository, usually located on a server somewhere (in this case, GitHub). “origin” is the default name git gives to a remote server (you can have multiple remotes), so git remote add origin tells git to add the default remote server URL for this repository.
Push to GitHub
git push -u -f origin mainThe -u (or --set-upstream) flag sets the remote origin as the upstream reference. This allows you to later do git push and git pull commands without having to specify the origin, as we always want GitHub to do in this case.
The -f (or –force) flag stands for force. It automatically rewrites everything in the remote directory. We use it here to overwrite the default README that GitHub automatically initializes.
All together
git init
git add -A
git commit -m 'Added my project'
git remote add origin [email protected]:sammy/my-new-project.git
git push -u -f origin mainDeploy a GitHub repository on DigitalOcean
Now that you have your GitHub repository, using the DigitalOcean app platform, easily deploy it with 1 click to bring it live.
Result
Now, you're ready to track your code changes remotely on GitHub! As a next step, use the Introduction to GitHub and Open Source Projects tutorial series to master GitHub.
You can use the Github cheat sheet and keep it as a reference.
Once you start collaborating with others on a project, you need to know how to create a pull request.