Introduction
DeepSeek R1 has taken the AI/ML community by storm in recent weeks, for good reason, and has even spread beyond it into the wider world, with major implications for economics and policy. This is largely due to the open-source nature of the model suite and the incredibly low price of training, which has shown the wider community that training SOTA AI models does not require nearly as much capital or dedicated research as previously thought.
In the first part of this series, we introduced DeepSeek R1 and showed how to run the model using Olama. In this follow-up, we’ll start with a deeper dive into what makes R1 truly special. We’ll focus on analyzing the model’s unique reinforcement learning (RL) paradigm to see how the reasoning capabilities of LLMs can be encouraged purely through RL, and then, we’ll talk about how distilling these techniques into other models allows us to share these capabilities with existing versions. We’ll end with a short demonstration of how to set up and run DeepSeek R1 models with GPU Droplets using GPU Droplets’ 1-Click Model.
Prerequisites
- Deep learning: This article covers intermediate to advanced topics related to training neural networks and reinforcement learning.
- DigitalOcean account: We will specifically use DigitalOcean's HuggingFace 1-Click Model GPU Droplets for testing R1.
DeepSeek R1 Overview
The DeepSeek R1 research project aimed to recreate the effective reasoning capabilities demonstrated by powerful reasoning models, namely OpenAI’s O1. To achieve this goal, they sought to improve their existing work, DeepSeek-v3-Base, using pure reinforcement learning. This led to the emergence of DeepSeek R1 Zero, which shows excellent performance on reasoning metrics, but lacks human interpretation capabilities and exhibits some unusual behaviors such as language mixing.
To improve these problems, they proposed DeepSeek R1, which involves a small amount of cold-start data and a multi-stage training pipeline. R1 achieved the readability and applicability of SOTA LLM by fine-tuning the DeepSeek-v3-Base model on thousands of cold-start data samples, then running another round of reinforcement learning, followed by supervised fine-tuning on the argument dataset, and finally finishing with a final round of reinforcement learning. They then distilled this technique to other models by supervising their fine-tuning on the data collected from R1.
Stay tuned for a deeper look at these development stages, and a discussion of how the model can be iteratively improved to reach the capabilities of DeepSeek R1.
DeepSeek R1 Zero Tutorial
To create DeepSeek R1 Zero, the base model from which R1 was developed, the researchers applied RL directly to the base model without any SFT data. Their chosen RL paradigm is called group relative policy optimization (GRPO). This process is adapted from the DeepSeekMath paper.
GRPO is similar to familiar and other RL systems, but it differs in one important way: it does not use a critical model. Instead, GRPO estimates the baseline from the group scores. Reward modeling has two rules for this system, each of which rewards the accuracy and adherence of the template to a pattern. The reward then serves as a source of training signals that are then used to change the direction of the RL optimization. This rule-based system allows the RL process to iteratively refine and improve the model.
The training template itself is a simple written format that guides the base model to follow our specified instructions as above. The model measures responses to the «announcement» set for each step of the RL. “This is a significant achievement, as it highlights the model’s ability to learn and generalize effectively through RL alone” (source).
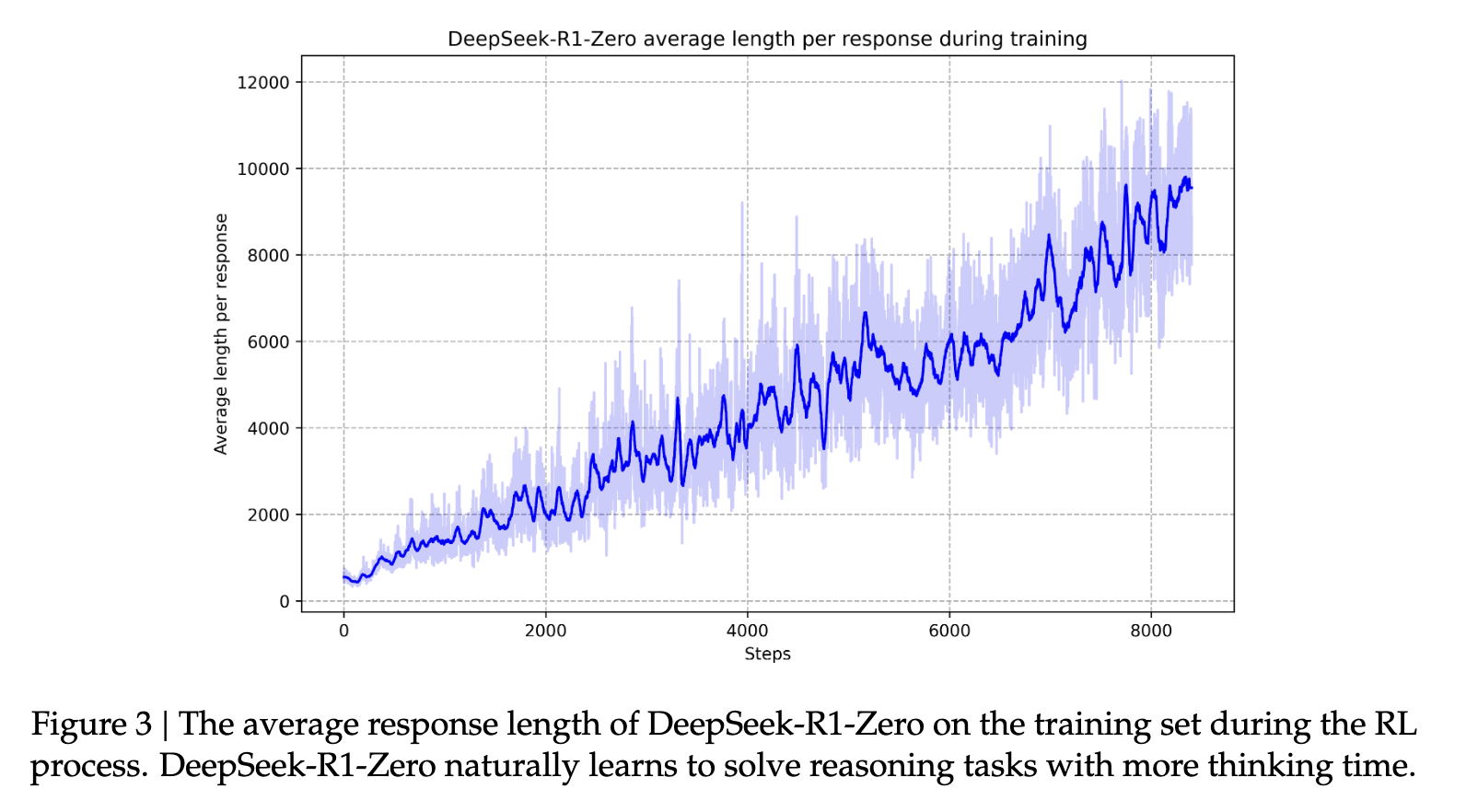
This self-evolution of the model leads it to develop powerful reasoning capabilities, including self-reflection and consideration of alternative approaches. This is reinforced by a moment during training that the model’s research team calls an “aha moment.” During this phase, DeepSeek-R1-Zero learns to devote more thinking time to a problem by reevaluating its initial approach. This behavior is not only a testament to the model’s growing reasoning abilities, but also a fascinating example of how reinforcement learning can lead to unexpected and complex results.» (Source).
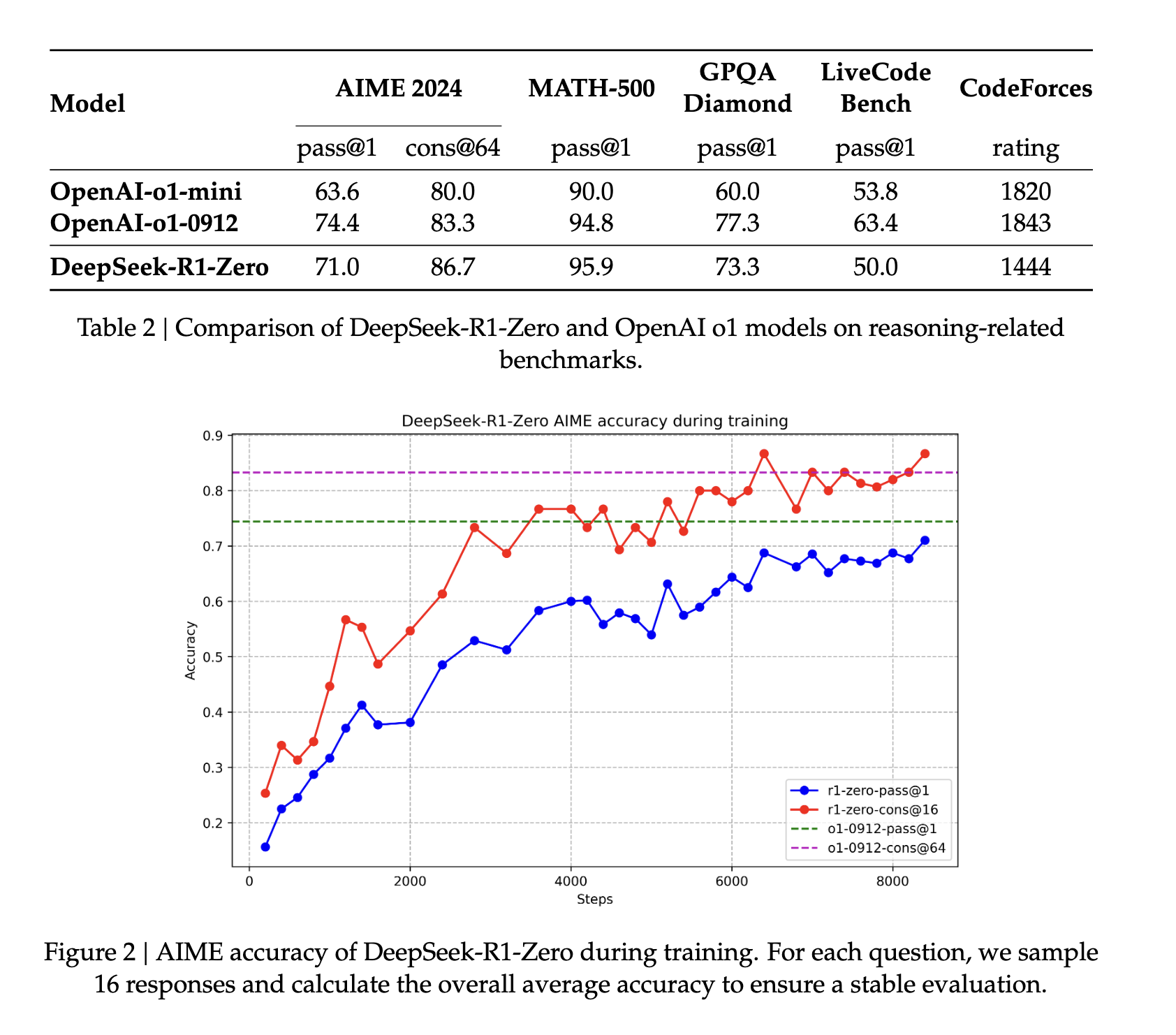
DeepSeek R1 Zero performed very well across the benchmarks, but suffered greatly in terms of readability and usability compared to proper, human-friendly LLMs. So the research team proposed DeepSeek R1 to better improve the model for human-level tasks.
From DeepSeek R1 Zero to DeepSeek R1
To go from the relatively untamed DeepSeek R1 Zero to the much more functional DeepSeek R1, the researchers introduced several training stages.
To begin with, DeepSeek-v3-Base was fine-tuned on thousands of cold-start data pieces before running the same RL paradigm used for DeepSeek R1 Zero with the added bonus of consistent language in the outputs. In practice, this step works to enhance the reasoning capabilities of the model, especially in reasoning tasks such as coding, mathematics, science, and logical reasoning, which involve well-defined problems with clear solutions (source).
Once this RL phase is complete, the resulting model is used to collect new data for supervised fine-tuning. «Unlike the initial cold-start data, which focuses primarily on reasoning, this phase combines data from other domains to enhance the model’s capabilities in writing, role-playing, and other general-purpose tasks» (source).
Next, the second stage of RL is implemented to improve “the usefulness and harmlessness of the model while simultaneously refining its reasoning capabilities” (source). By further training the model on various fast distributions with reward signals, they can train a model that excels at reasoning while prioritizing usefulness and harmlessness. This helps the models become “human-like” in their responsiveness. This helps the model evolve the incredible reasoning capabilities it is known for. Over time, this process helps the model develop long chains of thought and reasoning that characterize it.
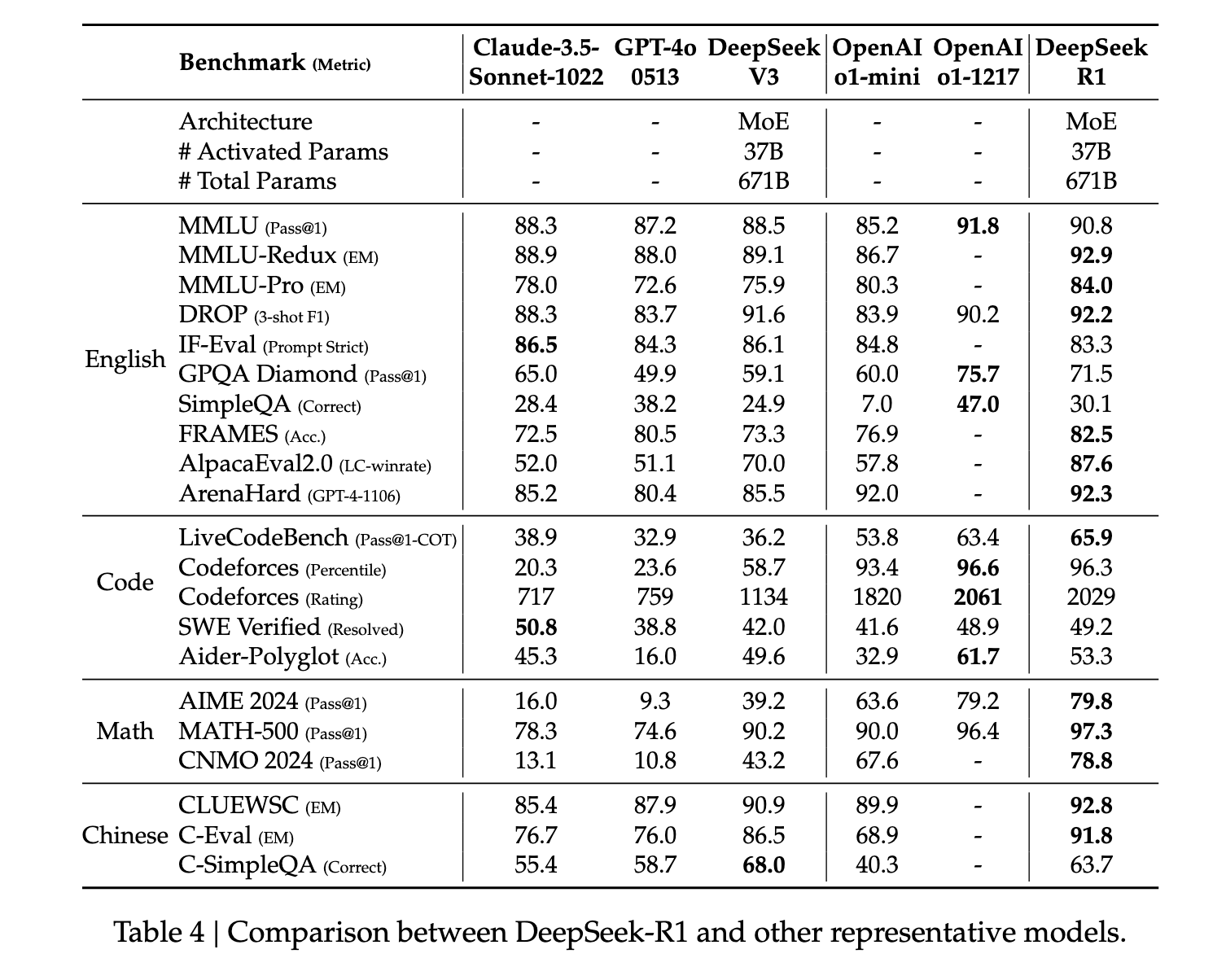
Across the board, R1 shows state-of-the-art performance on reasoning measures. In some tasks, such as math, it has even been shown to outperform published benchmarks for O1. Overall, there is also a very strong performance on stem-related questions, which is primarily attributed to large-scale reinforcement learning. In addition to STEM subjects, the model is highly skilled at answering questions, educational tasks, and complex reasoning. The authors argue that these improvements and increased capabilities are due to the evolution of chain-of-thought processing models through reinforcement learning. Long chain-of-thought data is used during reinforcement learning and fine-tuning to encourage the model to produce longer, more introspective outputs.
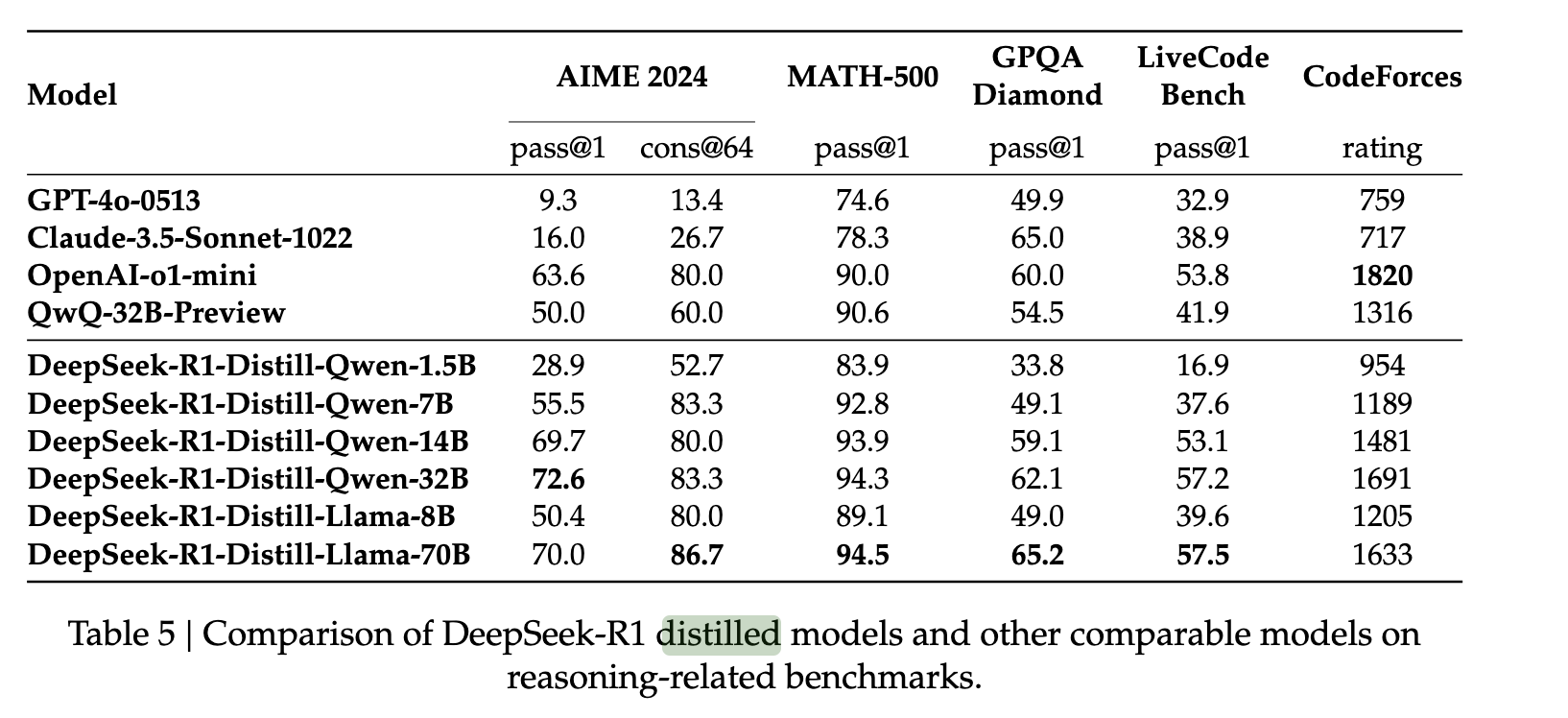
DeepSeek R1 Distilled Models
Launching DeepSeek R1 on GPU Droplets
Setting up DeepSeek R1 on GPU Droplets is very simple if you already have a DigitalOcean account. Be sure to log in before continuing.
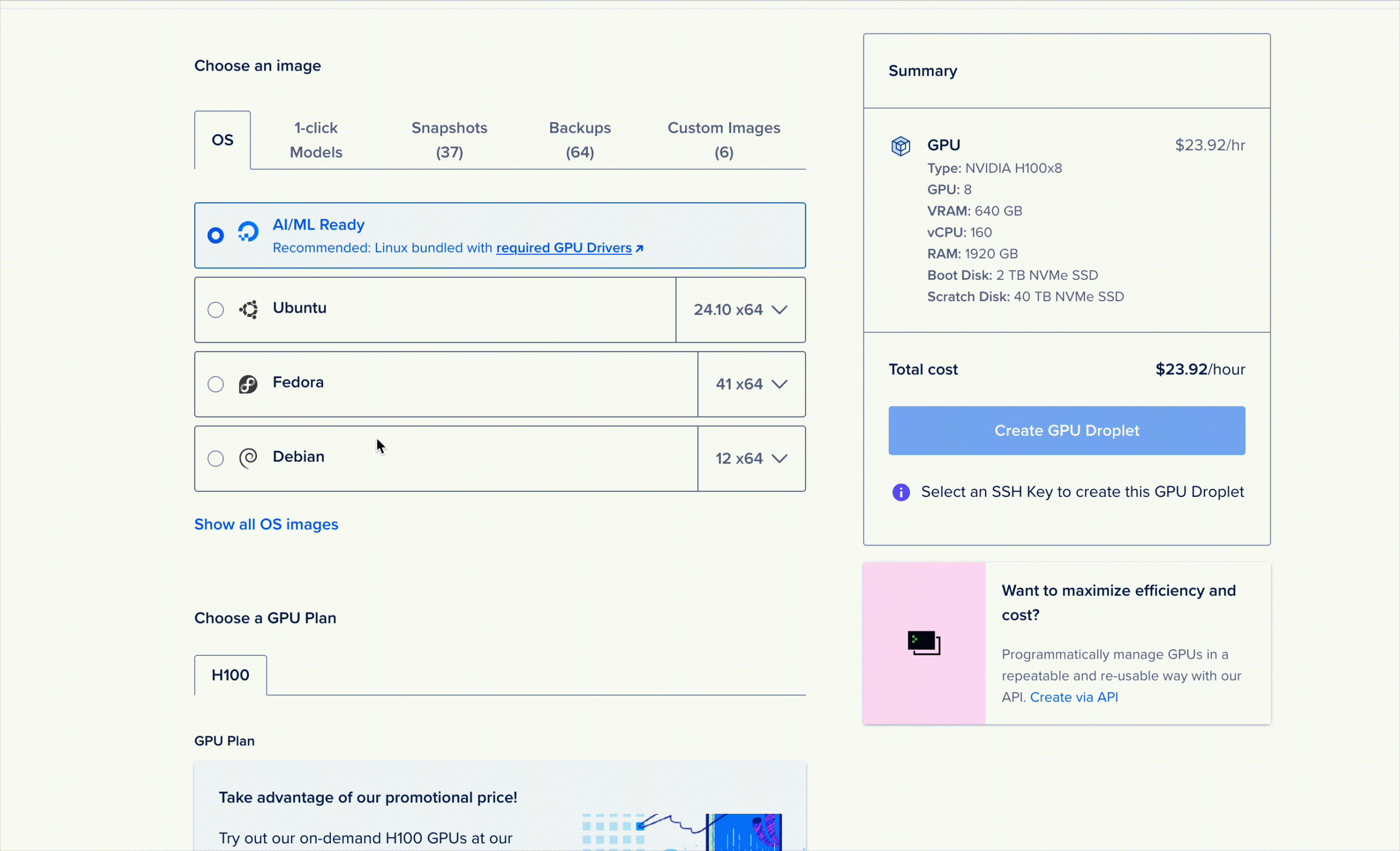
We provide access to R1 as a 1-Click Model GPU Droplet. To launch it, simply open the GPU Droplet console, go to the «1-Click Models» tab in the model selection window, and launch the device!
From there, the model will be accessible by following the HuggingFace or OpenAI methods to communicate with the model. Use the script below to interact with your model with Python code.
import os
from huggingface_hub import InferenceClient
client = InferenceClient(base_url="http://localhost:8080", api_key=os.getenv("BEARER_TOKEN"))
chat_completion = client.chat.completions.create(
messages=[
{"role":"user","content":"What is Deep Learning?"},
],
temperature=0.7,
top_p=0.95,
max_tokens=128,
)
## or use OpenAI formatting
#import os
#from openai import OpenAI
#
#client = OpenAI(base_url="http://localhost:8080/v1/", api_key=os.getenv("BEARER_TOKEN"))
#
#chat_completion = client.chat.completions.create(
# model="tgi",
# messages=[
# {"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
# {"role": "user", "content": "What is Deep Learning?"},
# ],
# temperature=0.7,
# top_p=0.95,
# max_tokens=128,
#)Alternatively, we have created a custom personal assistant that runs on the same system. We recommend using the personal assistant for these tasks because it abstracts away a lot of the complexity of interacting directly with the model by putting everything in a nice GUI window. For more information on using the personal assistant script, please check out this tutorial.
Result
In conclusion, R1 is a step forward for the LLM development community. Their process promises to save millions of dollars in training costs while delivering performance comparable to or even better than advanced closed source models. We will be watching DeepSeek closely to see how they continue to grow as their model gains international recognition.