Introduction
Apache is a free and open source web server software developed by the Apache Software Foundation and freely available to the Internet community. It generally listens for HTTP requests on port 80 and serves HTML documents. Thanks to its modular structure, a wide range of functions can also be embedded. A combination of databases such as MySQL and server-side scripting languages such as PHP, Perl, and Python are commonly used to create dynamic pages. As the most popular web server in the world, the Apache HTTP Server is part of a diverse software package that also includes LAMP, MAMP, WAMP, and XAMPP. However, in this tutorial, we will focus on how to install and configure the web server as a single component.
Installation and setup
All you need to get Apache on your Windows PC is the appropriate Apache software package for your operating system. The Apache Software Foundation only provides the source code on its website. You can also find executable binaries for Windows on community pages such as Apache Lounge and Apache Haus. This tutorial is based on Apache version 2.4.20 for 64-bit systems, which is available from Apache Lounge. To use Apache with Windows, no installation is required. Instead, you can do the following:
- Save the software package as a ZIP file in any folder on your local Windows PC.
- Unzip the ZIP file by double-clicking the folder icon.
- Name the file Apache24 and copy it to C:\.
You can now find all the files needed to set up your local Apache web server in the C:\Apache24 folder.
Trial run
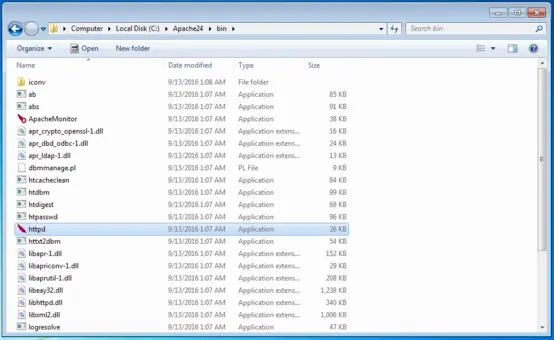
After installation, it is recommended to do a test run. To do this, first open C:/Apache24 and open the bin file. This is where you will find the httpd program. Double-click to start your Apache web server.
Then your system will usually display two error messages indicating that software components must be installed and that the Apache web server is blocked by the operating system firewall.
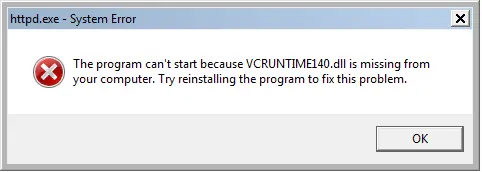
httpd.exe system error
If this is the first time you are installing Apache on your Windows PC, your system will probably report that the VCRUNTIME140.dll file is not found and therefore the web server will not start.
These errors can be corrected by installing the required software components. Apache is written in C++, which means that a program when used on a Windows operating system requires a suitable runtime environment. This is available through the Visual C++ compiler software. Missing runtime components can be installed with the Visual C++ redistributable packages. These are available for free download from the Microsoft website and can be installed by simply double-clicking on the .exe file.
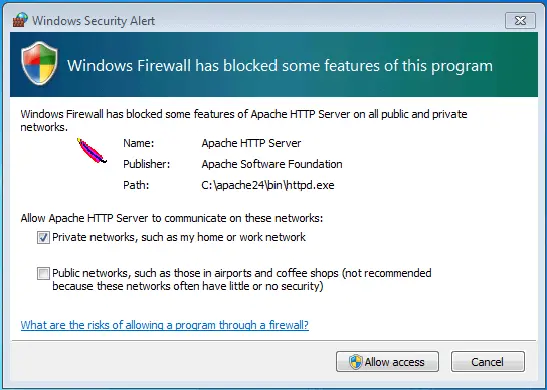
Windows Security Alert
Generally, personal computers are protected by a firewall, which prevents unauthorized external programs from accessing the system via the network. However, if you want to make your local Apache HTTP server available on a home or work network, you must explicitly allow Apache to communicate. This can be done in the following security message, which reports that some web server functions are blocked by the firewall.
If you want to allow access to your server on one of the specified networks, check the corresponding box and click the "Allow Access" button. This usually requires administrative rights.
Once you have installed the required runtime components and configured the firewall settings to your specific model, using the Apache HTTP server in its standard configuration is no longer an obstacle. Restart the web server by double-clicking on the httpf file. A black command prompt window will automatically open. If you want to terminate the Apache web server, close the window by clicking the x in the upper right corner.
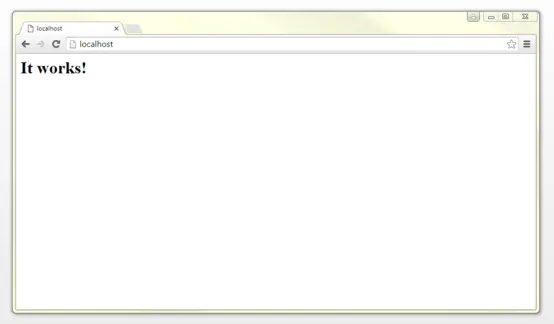
To access your web server, simply enter "localhost" or the standard IP address, "127.0.0.1" into the search bar of any web browser.
If all settings are entered correctly, the web browser will display a default index.html with the phrase "This works!", then you can configure your web server.
Configuration
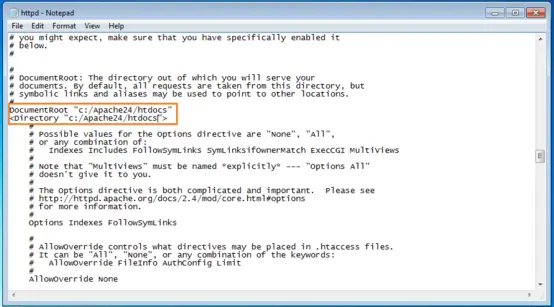
The Apache http server is generally pre-configured as a software package in a way that makes it work without any further configuration. All content that is supposed to be accessible through the web server is stored in a folder called DocumentRoot in the httpd.conf configuration file. By default, this is the htdocs folder in C:\Apache24.
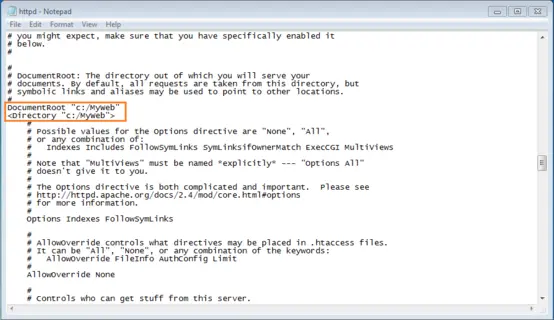
If you want to store your website documents and files in a different folder, you need to enter it in httpd.conf as «DocumentRoot» and «Directory».
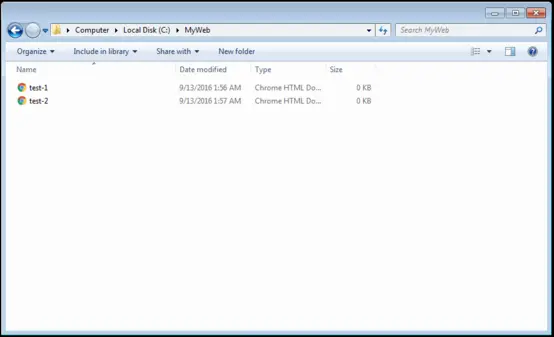
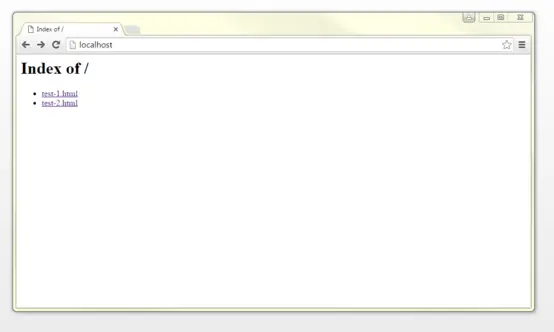
For this demonstration, we have created a new folder called MyHomepage in the C:\ directory. This will act as a web page folder for a fictional website. Two HTML documents: test-1 and test-2 are stored in this file.
Now we will adapt the «DocumentRoot» and «Directory» information for our new website folder by replacing both instances of «C:/Apache24/htdocs» with «C:/MyHomepage».
To access the web server, Apache must first be restarted via localhost. Then the web browser will display the website folder listing with the HTML pages, test-1.html and test-2.html.