Introduction
Knowing how to work with arrays in shell scripts will help you work with larger data sets in a very efficient manner. But what are arrays and how do you create an array? Let's find out.
What are arrays?
If you already have a basic understanding of any programming language, you know what arrays are. But for those unfamiliar, let's go over the basics of arrays and learn how to work with them.
Variables store single data elements. Arrays, on the other hand, can store an almost unlimited number of data elements. When working with large amounts of data, variables can be very inefficient, and using arrays is very useful.
Let's learn how to create arrays in shell scripts.
Creating arrays in shell scripts
There are two types of arrays that we can work with in shell scripts.
- Indexed arrays – store elements with an index starting at 0
- Associative arrays – store elements in key-value pairs
The default array created is an indexed array. If you specify index names, it becomes an associative array, and elements can be accessed using index names instead of numbers.
Declaring arrays:
root@ubuntu:~# declare -A assoc_array
root@ubuntu:~# assoc_array[key]=value
OR
root@ubuntu:~# declare -a indexed_array
root@ubuntu:~# indexed_array[0]=valueNote the uppercase and lowercase a. The uppercase A is used to declare an associative array while the lowercase a is used to declare an indexed array.
The declare keyword is used to explicitly declare arrays, but you don't really need to use them. When you're creating an array, you can simply initialize the values based on the type of array you want without explicitly declaring the arrays.
Working with arrays in shell scripts
Now that you know how to create an array, let's learn how to work with arrays. Since these are collections of data elements, we can work with loops and arrays at the same time to extract the required data points.
1. Accessing array elements individually
Since we know that each data point is indexed individually, we can access all the elements of the array by specifying the array index as shown below:
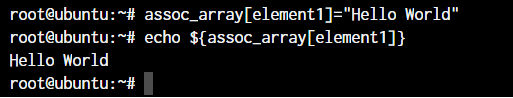
assoc_array[element1]="Hello World"
echo ${assoc_array[element1]}Similarly, let us access some elements of an indexed array. We can specify all the elements of the indexed array by separating them with spaces, as the index is automatically generated for each of those elements.
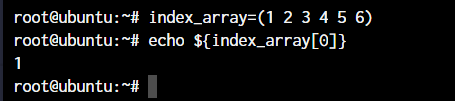
index_array=(1 2 3 4 5 6)
echo ${index_array[0]}As you can see, the first element is automatically printed at index 0.
2. Reading array elements sequentially
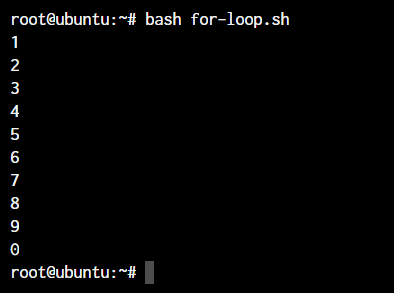
If you already know loops, this will be easy. If not, we'll cover them in a future tutorial. We'll use while or for loops in shell scripts to operate on array elements. Copy the following script and save it as Save .sh
#!/bin/bash
index_array=(1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0)
for i in ${index_array[@]}
do
echo $i
doneThe above script will have the following output:
Now you may have noticed index_array[@] and if you are wondering what the @ symbol is for, we will cover that right now.
Built-in operations for arrays in shell scripts
Now that you've learned how to access elements individually and use for loops, let's learn the various operations that are available by default for arrays.
1. Access all elements of an array
We learned how to access elements by providing an index or array key. But if we want to print all the elements at once or work with all the elements, we can use another operator which is the [@] sign.
As you noticed in the example above, I used this symbol when I wanted to loop through all the elements of the array using a for loop.
echo ${assoc_array[@]}The above prints all the elements stored in the assoc array.
2. Count the number of elements in an array
Similar to the @ symbol above, we have the symbol # which can be prefixed to an array name to give us the number of elements stored in the array. Let's see how it works.
echo ${#index_array[@]}If you want to count the number of characters used for a particular element, we can simply replace the @ sign with the index.
3. Delete individual array elements
We know how to add elements of an array and print them as well. Let's learn how to remove specific elements. For this purpose we use the unset keyword.
unset index_array[1]Replace the array name and index ID in the code example above and you have deleted the array element you want. Pretty simple, right?
Result
Shell scripts are very extensive and can replace any function you can perform in the terminal with the right person writing the script. Some additional capabilities of arrays in shell scripts also include the ability to work with regex (regular expressions). We can use various regular expressions to manipulate array elements in shell scripts.
By now, we hope you have a good understanding of creating and working with arrays and can use arrays in your scripts. Leave a comment below to share your thoughts and let us know if you have any questions about this topic.