Introduction
Next.js is a popular React framework for easily building server-rendered React applications. In this tutorial, we will walk through deploying a Next.js application on a DigitalOcean droplet using Nginx as a reverse proxy. This step-by-step guide assumes that you have a ready-to-deploy Next.js application and a DigitalOcean account.
Prerequisites
- A Next.js application
- A DigitalOcean account
- Registered domain name (optional but recommended)
- Local installation of Node.js and npm or yarn
Step 1: Create a digitalocean Droplet
We will host our Next.js application on a DigitalOcean Droplet that we will configure ourselves. Let's create the droplet now.
- Log in to your DigitalOcean account and go to the Droplets section.
- Click “Create DROPLET”.
- Select the Ubuntu image (preferably the latest LTS version).
- Choose the desired droplet size according to your needs and budget.
- For better performance, choose the closest data center area to your target audience.
- Add your SSH keys for secure access to your droplet.
- Choose a hostname for your droplet, which can be your domain name or any preferred name.
- Click “Create DROPLET”.
- Create the Droplet
After creating the Droplet, note the IP address assigned to it.
Step 2: Launch the Droplet
Now that we have created the droplet, we need to prepare it so that it can accept incoming connections and route those connections to our Next.js application.
SSH into your droplet using the IP address and SSH key you provided during droplet creation:
ssh root@<DROPLET_IP>
Update and upgrade packages in Droplet:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
Install the required packages:
sudo apt install -y nodejs npm nginx
Step 3: Configure Nginx
Nginx is the tool that handles all the routing to our Next.js application. Create a new Nginx configuration file for your Next.js application:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/nextjs
Paste the following configuration, replacing server_name with your droplet domain name or IP address:
server {
listen 80;
server_name YOUR_IP_ADDRESS;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:3000;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection 'upgrade';
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade;
}
}Save and close the file. Create a symbolic link to activate the configuration:
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/nextjs /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
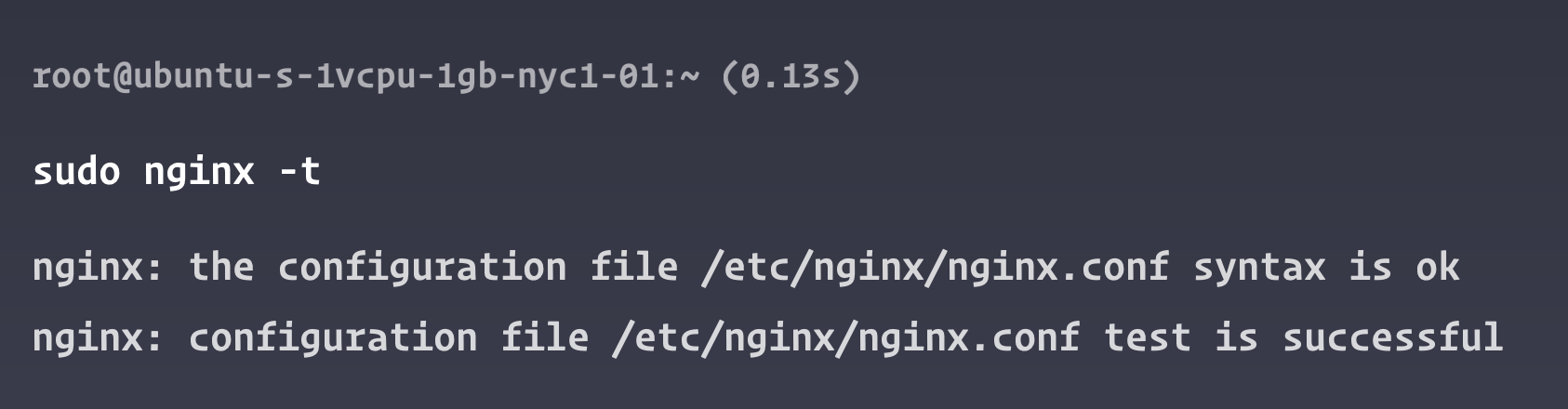
Test the Nginx configuration for any syntax errors:
sudo nginx -t
If the configuration test was successful, restart Nginx:
sudo service nginx restart
Step 4: Deploy the Next.js application
Next, we get a Next.js application into the Droplet. There are many options for doing this.
- Create an SSH key on the server, connect it to your GitHub account, and clone your repository.
- Create a Next.js application in Droplet
For this tutorial, we will create a new Next.js application in our Droplet.
SSH back into your droplet:
ssh root@<DROPLET_IP>
Create a new Next.js application and follow the instructions:
cd /var/www
npx create-next-app nextjsGo to the Next.js application directory:
cd nextjs
Install the program dependencies:
npm install
Build the Next.js application:
npm run build
Finally, run the Next.js application:
npm start
Your Next.js application is now deployed and accessible on your droplet domain name or IP address. To have your application run in the background and automatically restart when the server crashes or restarts, you will need to use a process manager like PM2.
Step 5: Launch PM2 Process Manager
We started npm from within our Droplet. Sometimes this command may stop running for reasons like a server restart or an update needing to be installed. We will use a tool called PM2 to make sure our Next.js application is always running. PM2 will restart even if the Next.js application crashes.
To install PM2 globally on your droplet:
sudo npm install -g pm2
Go to the Next.js application directory (if it's not there already):
cd /var/www/nextjs
Start the Next.js application using PM2:
pm2 start npm --name "nextjs" -- start
This command starts the Next.js application named “nextjs” using the npm start command. PM2 will automatically restart the application if the server crashes or restarts.
To ensure PM2 starts at boot, run:
pm2 startup
This command will create a script that you can copy and paste into your terminal to start PM2 at boot time.
Save current PM2 processes:
pm2 save
Result
You have now successfully run a Next.js application on a DigitalOcean droplet using Nginx as a reverse proxy and PM2 as a process manager. Your application should be accessible at your droplet's domain name or IP address.
If you are using a domain name, remember to configure your DNS settings. Point your domain's A record to your droplet's IP address so you can access the application using the domain name.
For improved security and SEO, consider setting up SSL certificates using Let's Encrypt and implementing HTTPS connections. Additionally, you can explore optimizing your Next.js application with caching and other performance improvements.