Introduction
In this article, we are going to talk about changing the SSH port on a Linux VPS and how to choose the right port. Secure Shell, also known as SSH credentials, is a network protocol that allows you to access a server remotely. You can also use the SSH protocol to encrypt the communication between the server and yourself to increase the security of your information.
However, using standard Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) port 22 for SSH can be dangerous because this port is highly vulnerable to many cyber threats, such as brute-force attacks, and hackers can infiltrate your sensitive encrypted data through this port.
To prevent such incidents and protect your SSH server, you should be able to change your port. In this article, we are going to explain the easiest way to choose and change the SSH port on a Linux VPS. Stay tuned for more.
Choosing a new SSH port
When choosing a new SSH port for your Linux virtual server, keep in mind that port numbers 0 to 1023 are reserved for special services and you can only access them with root access.
How to change default SSH ports
In this section, we will explain how to change the SSH port on a Linux VPS in 4 very simple and easy steps.
Step 1: Connect to the server via SSH
Connect to your server via SSH, you can run the following code in Terminal or PuTTy:
In the above command, replace username with your username and replace 0.0.0.0 with your server address. For example:
After executing the above command, you will be asked to enter your SSH password or keys. After entering the password or key and pressing ENTER, the SSH connection to the server will be established.
Step 2: Change SSH settings
By running the following command, you will access the SSH daemon, or sshd:
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
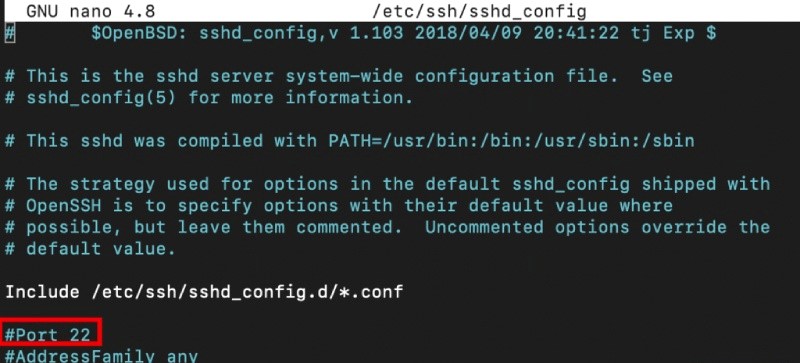
After running the above command, the SSH configuration file will open. At this point in changing the SSH port on your Linux VPS, you should look for a line that reads #Port 22. Remove the number and the # sign and replace it with the desired SSH port number that you want to use. For example, after running the above command, you will see the following output:
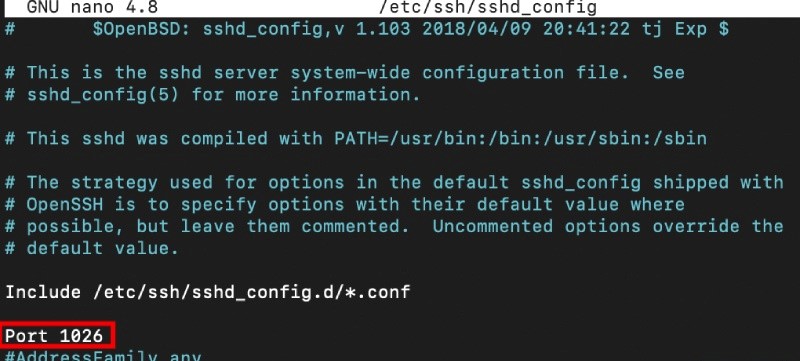
Change the port number to 1026:
Then, save the changes.
Step 3: Configure the firewall
By configuring your firewall, you can rest assured that new ports will not be blocked. If you are setting up a new VPS, all ports should be open by default.
In this step, the first thing you need to do is update your firewall settings to allow incoming connections to the new port. To get a good feel for this step, let’s assume we are going to use the UFW firewall. In the next step of changing the SSH port on your Linux VPS, you need to run the following command from the command line:
sudo ufw allow 1026/tcp
Then, restart the SSH service using the following command:
- In Debian and Ubuntu distributions
sudo service ssh restart
- In Debian and Ubuntu distributions with systemd
sudo systemctl restart ssh
- On CentOS and Fedora
sudo service sshd restart
- On CentOS and Fedora with systemd
sudo systemctl restart sshd
Step 4: Test the new default port
To make sure the new SSH port is open, run the ss or netstat command at the command prompt. The ss command looks like this:
ss -tulpn | grep 1026
The output of the above command is as follows:
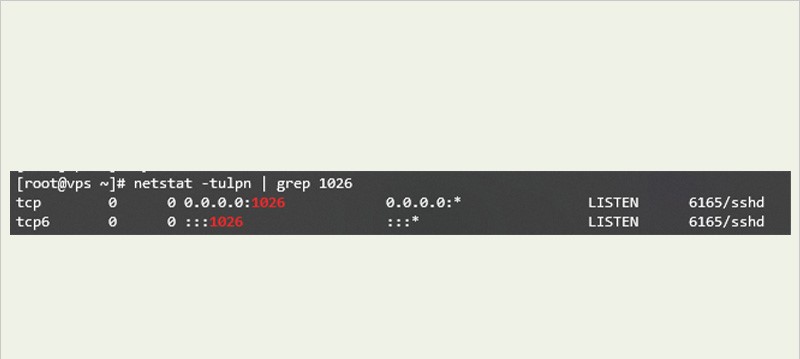
The netstat command is as follows:
netstat -tulpn | grep 1026
The output of the above command is as follows:
Now you can run the following command at the command line to log in to SSH:
ssh -p [port] user@server
Replace [port] with the port number, replace user with the username, and replace server with the server address. For example:
ssh -p 1026 [email protected]
Result
Using the default SSH port 22 compromises your security and makes you an easy target for hackers. Hackers usually look for open ports to intercept and extract sensitive data. As a result, we recommend that you change your SSH port as soon as possible to minimize the possibility of cyber attacks and protect your Linux server. First of all, note that ports 0 to 1023 are reserved for special services. As a result, it is better to choose your port number from 1024 to 65535. After configuring the SSH daemon and updating the firewall settings, restart your SSH service and test the connection to the new port.